Smart Engineering Documentation
Smart Engineering Documentation is a powerful feature that automatically generates comprehensive technical documentation for your codebase. By analyzing your source code, it creates detailed documentation including architecture diagrams, API references, and business logic explanations.
Overview
The Smart Engineering Documentation menu provides a complete workflow for:
- Creating Projects - Set up new documentation projects for your codebases
- Managing Organizations - Work with multiple organizations and their projects
- Generating Documentation - Automatically create full technical documentation
- Managing Tasks - Track and regenerate documentation tasks
- Downloading Artifacts - Export documentation in various formats
Access Smart Engineering Documentation from the AI Cockpit sidebar to start generating professional documentation for your projects.
Getting Started
Organization Selection
Before creating or managing projects, you must select an organization:
- Open the Smart Engineering Documentation menu
- Use the Organization Selector dropdown at the top
- Select your organization from the list
- All projects will be filtered by the selected organization
The organization selector persists your choice across sessions. Projects are always associated with a specific organization.
Creating a New Project
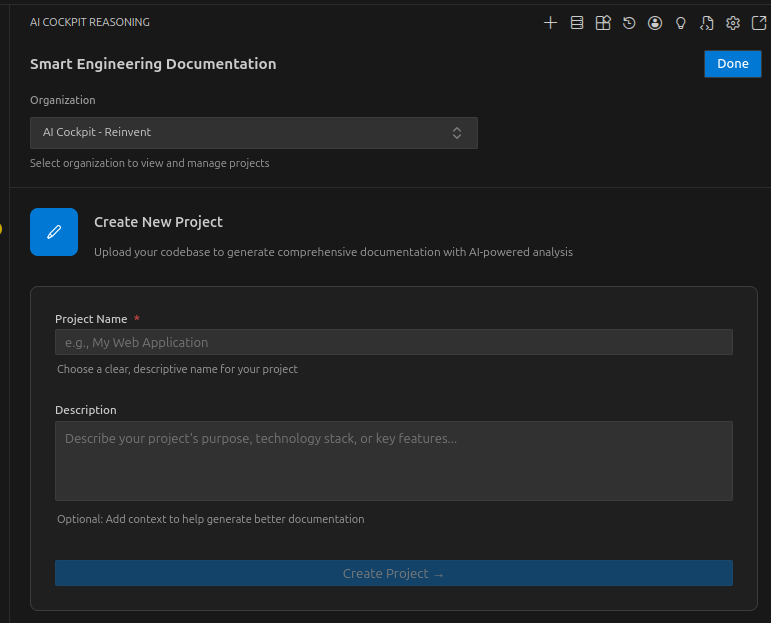
Step 1: Project Information
To create a new documentation project:
-
Enter a Project Name (required)
- Use a descriptive name that identifies your codebase
- Example: "E-commerce Backend API"
-
Add a Project Description (optional)
- Provide context about the project
- Include key technologies or frameworks used
- Example: "Node.js REST API for e-commerce platform with MongoDB"
-
Click Create Project to proceed
Ensure you have selected the correct organization before creating a project, as this cannot be changed later.
Step 2: Upload Source Code
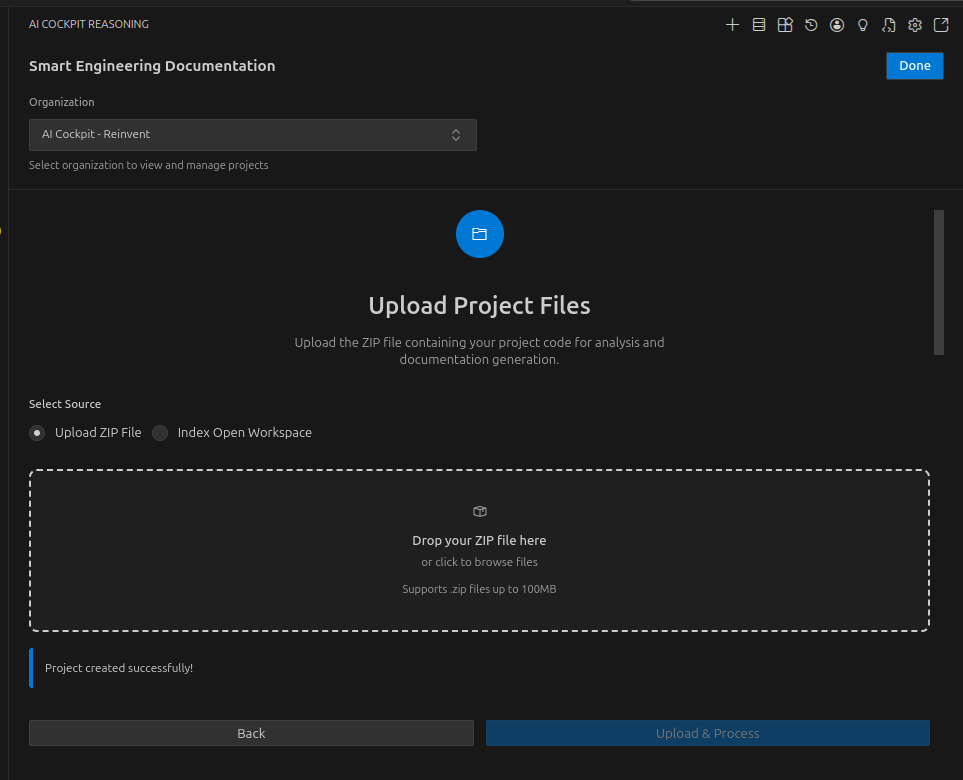
After creating the project, you need to upload your source code. There are two methods:
- ZIP File Upload
- Workspace Indexing
Upload a ZIP File:
- Click Choose File or drag and drop
- Select a
.zipfile containing your source code - Ensure the ZIP includes all relevant source files
- Click Upload to start processing
- Include all source code files
- Exclude
node_modules,vendor, or similar dependency directories - Keep the ZIP file under 100MB for optimal processing
- Include configuration files and documentation
Index Current Workspace:
- Click Index Workspace button
- The system will automatically create a ZIP from your open VSCode workspace
- Files matching
.gitignorepatterns will be excluded - Upload starts automatically after ZIP creation
Workspace indexing respects your .gitignore file and excludes common build artifacts and dependencies automatically.
Step 3: Automatic Documentation Generation
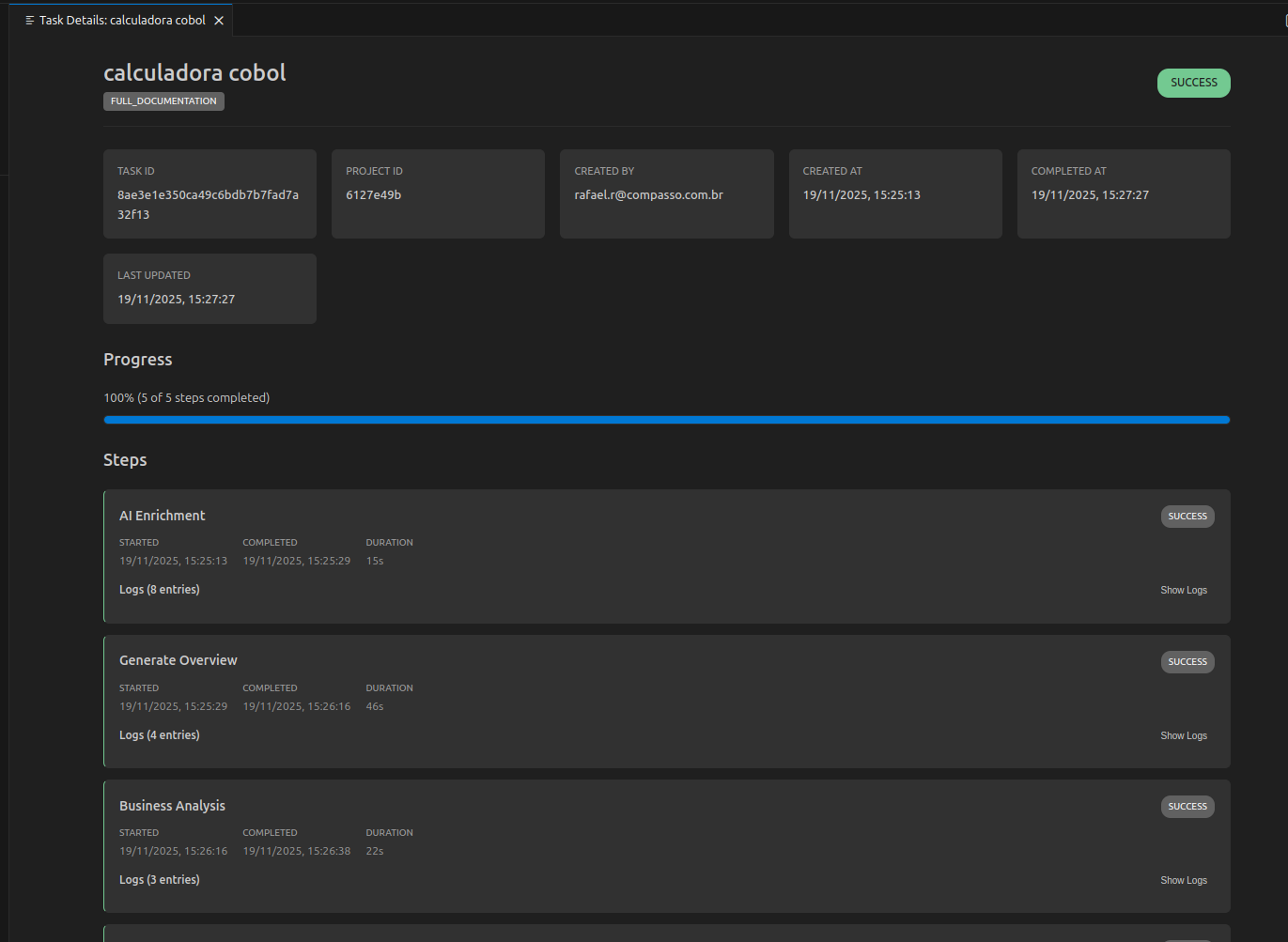
Once the source code is uploaded:
- The project status changes to Processing
- The system analyzes your codebase structure
- When ready, Full Documentation generation starts automatically
- A detailed progress page opens showing generation steps
The initial processing time depends on your codebase size. Small projects (< 1000 files) typically complete in 2-5 minutes.
Managing Existing Projects
Projects List
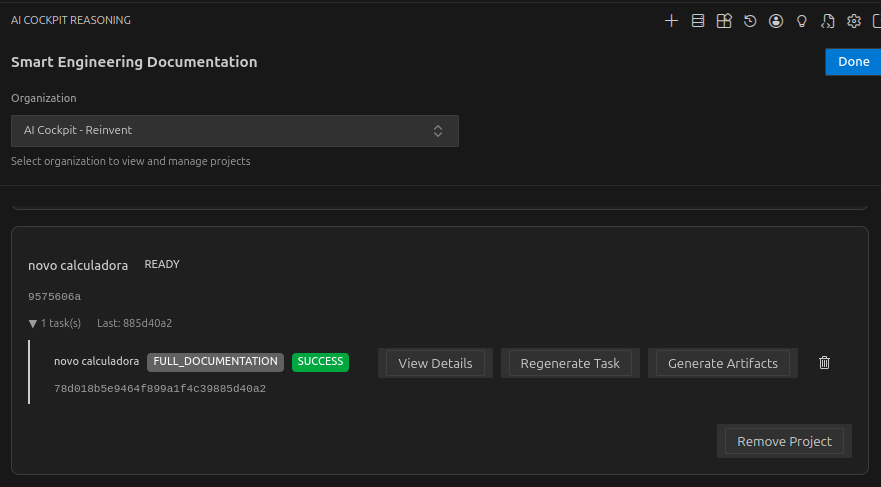
The Existing Projects section displays all projects for the selected organization:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Project Name | The name of the project |
| Status | Current project state (Ready, Processing, Failed) |
| Tasks | List of documentation tasks for the project |
| Actions | Available operations for the project |
Project Actions
Each project card provides several actions:
View Details
Click View Details to open a detailed page showing:
- Project information and metadata
- Complete task history
- Generation progress and logs
- Error messages (if any)
Generate Full Documentation
Available when:
- Project status is Ready
- No documentation task exists yet
Clicking this button:
- Starts a new full documentation generation task
- Opens the task details page automatically
- Shows real-time progress updates
Regenerate Task
Available for existing tasks. This action:
- Creates a new documentation generation task
- Uses the same source code
- Applies current LLM configuration
- Opens task details page for monitoring
Regenerate documentation when:
- You've updated your LLM model configuration
- Previous generation had errors
- You want to improve documentation quality
- Source code analysis needs updating
Generate Artifacts
Available when:
- Project status is Ready
- Full documentation task is Completed
This generates downloadable artifacts including:
- Markdown Documentation - Complete documentation in MD format
- HTML Documentation - Interactive HTML version
- Diagrams - Architecture and flow diagrams
Download Artifacts
Once artifacts are generated:
- Click Download button
- Artifacts open automatically in VSCode
- Files are saved to your local disk
- HTML documentation can be viewed in browser
Downloaded artifacts include an index.html file that provides a navigable documentation website.
Reupload Source Code
To update the project with new source code:
- Click Reupload button
- Select a new ZIP file or index workspace
- Project status changes to Processing
- After processing completes, documentation regenerates automatically
- Task details page opens for monitoring
Reuploading source code will replace the existing codebase. Previous documentation tasks remain available for reference.
Delete Project
To remove a project:
- Click Delete button
- Confirm the deletion
- All associated tasks and artifacts are removed
Project deletion is permanent and cannot be undone. Download any important artifacts before deleting.
Task Management
Task List
Each project can have multiple documentation tasks:
- Full Documentation - Complete codebase documentation
- Docs - API and code documentation only
- Backlog - User stories and requirements extraction
Task Status
Tasks can have the following statuses:
| Status | Description | Actions Available |
|---|---|---|
| Running | Task is currently processing | View Details |
| Completed | Task finished successfully | View Details, Generate Artifacts, Download |
| Failed | Task encountered an error | View Details, Regenerate |
| Not Found | Task expired or was deleted | Regenerate |
Task Actions
View Task Details
Opens a detailed page showing:
- Current progress percentage
- Step-by-step execution log
- Processing stages and substeps
- Error messages (if failed)
- Estimated completion time
Regenerate Task
Creates a new task with the same configuration:
- Click Regenerate on the task
- New task starts immediately
- Task details page opens automatically
- Previous task remains in history
Delete Task
Remove a task from the project:
- Click Delete on the task
- Confirm deletion
- Task and its artifacts are removed
You cannot delete a task that is currently running. Wait for completion or failure before deleting.
Documentation Generation Process
Generation Stages
The documentation generation process includes several stages:
-
Code Analysis
- Parsing source files
- Identifying code structure
- Extracting dependencies
-
Symbol Extraction
- Classes and interfaces
- Functions and methods
- Variables and constants
-
Documentation Generation
- API documentation
- Architecture descriptions
- Business logic explanations
-
Diagram Creation
- Architecture diagrams
- Flow charts
- Dependency graphs
-
Artifact Compilation
- Markdown files
- HTML generation
- Asset bundling
Progress Monitoring
While documentation generates:
- Real-time progress percentage
- Current stage and substep
- Estimated time remaining
- Detailed execution logs
Keep the task details page open to monitor progress. The page updates automatically every 15 seconds.
Best Practices
Project Organization
- ✅ Use descriptive project names
- ✅ Include comprehensive descriptions
- ✅ Group related projects by organization
- ✅ Maintain one project per codebase
- ✅ Regularly update source code
Source Code Preparation
- ✅ Include all relevant source files
- ✅ Exclude dependency directories
- ✅ Keep ZIP files under 100MB
- ✅ Include README and configuration files
- ✅ Ensure code is well-structured
Documentation Management
- ✅ Regenerate after significant code changes
- ✅ Download artifacts for offline access
- ✅ Review generated documentation for accuracy
- ✅ Use latest LLM models for best results
- ✅ Keep task history for reference
Performance Optimization
- ✅ Remove unnecessary files before upload
- ✅ Use workspace indexing for active projects
- ✅ Generate artifacts only when needed
- ✅ Delete old projects to save space
- ✅ Monitor task progress regularly
Troubleshooting
Project Processing Failed
If project processing fails:
- Check the project details for error messages
- Verify the ZIP file contains valid source code
- Ensure the ZIP is not corrupted
- Try reuploading with a smaller codebase subset
- Contact support if the issue persists
Documentation Generation Failed
If documentation generation fails:
- Open task details to view error logs
- Check if the codebase structure is supported
- Verify LLM configuration is correct
- Try regenerating the task
- Consider using a different LLM model
Artifacts Not Available
If artifacts cannot be generated:
- Ensure the documentation task completed successfully
- Check project status is Ready
- Verify you have sufficient permissions
- Try regenerating the documentation
- Check for error messages in task details
Download Issues
If artifact download fails:
- Check your internet connection
- Verify the download URL is still valid
- Try downloading again after a few minutes
- Check VSCode output panel for errors
- Ensure you have write permissions to the download location
Advanced Features
Multiple Organizations
Work with multiple organizations:
- Switch between organizations using the selector
- Each organization has its own project list
- Projects are isolated by organization
- Permissions are organization-specific
Task History
Access complete task history:
- View all previous documentation generations
- Compare different task results
- Track documentation evolution
- Audit generation attempts
Custom LLM Configuration
Configure LLM settings for documentation:
- Choose different AI models
- Adjust output language
- Customize generation parameters
- Optimize for specific use cases
Next Steps
Now that you understand Smart Engineering Documentation, explore:
- Custom Modes - Create specialized documentation modes
- Settings Management - Configure LLM and output preferences
- MarketPlace - Discover additional documentation tools